- The task of a pull up or pull down resistor is to give a default value to a pin of a circuit component when there is no other connection is present. So, we are making the particular pin not to float!.
- Have a look at this circuit:
- Now, when S1 switch OFF, the input '1' is floating and it can take any value because of noise. So, we cannot really predict what will be there at the output '2'.
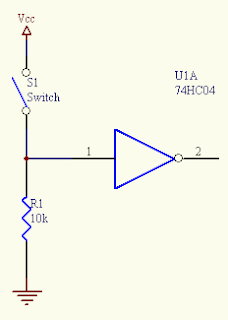
- To avoid this kind of behavior we attach a pull up resistor as follows:
- Now, when the S1 switch is OFF the pin '1' takes the Vcc voltage because normally the component does not absorb any current (high impedance inputs).
- Pull down resistor does essentially the same job.
I2C
- I²C requires pull-up resistors on its clock (SCL) and data line (SDA).
- The reason is because the pins on the chips are of open-collector design, which means that a chip can only pull the lines low, otherwise they float up to VDD.
- In I²C, pulling the line to ground indicates a logical zero while letting it float to VDD is a logical one.
- Pull up resistors help nodes to determine whether the other nodes are transmitting or not by monitoring the state of the line.
- When a node is transmitting it will the pull the line down to zero. Then the first node can detect that the other is transmitting.
[images credit: http://www.seattlerobotics.org/encoder/mar97/basics.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pull-up_resistor]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pull-up_resistor]